Date
Topics
Assignment
A4 - 23 days - ends Apr 28
Welcome Back!
- Review - Work:
- Ch 8 (p. 262) #109-115odd
- Ch 9 (p. 298) #37, 39, 43, 45 (Note: The y-axis passes through m1 and m3, not m1 and m4.), 47
Ch 9 Rotation
- 9-3 Calculating the Moment of Inertia
- Rotational inertia of a particle
- Iparticle = mr2
- Rotational inertia of a system of particles
- Rotational inertia of an extended body
- Parallel Axis Theorem: I = Icm + Mh2
- Moment of Inertia of Common Shapes (Table 9-1, p. 274)
- 9-4 Newton's Second Law for Rotation
- Torque - "turning force"
- depends on:
- amount of force
- more force more rotational acceleration
- direction of force
- force perpendicular to radius - maximum acceleration
- force parallel to radius - no acceleration
- where the force is applied
- more radius - more rot. acceleration
- amount of force
- Calculating torque
- (see Fig. 9-18 p. 280)
- Actually
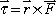
- direction: right-hand rule (torque is an axial vector)
- in problem solving, counterclockwise is +, clockwise is - (by convention)
- Even though torque has units N.m, torque is not measured in Joules - torque is a vector, work is a scalar.
- Torque = force times "lever arm"
- depends on:
- Newton's Second Law:
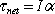
- Torque - "turning force"
- 9-5 Applications of Newton's Second Law for Rotation
- Note: You have to account not only for all of the forces on an object, but where on the object the forces are applied
- Rod pivoted at one end (see examples 9-6 and 9-9)
- Accelerating a flywheel (see example 9-8)
- Massive pulleys (see examples 9-10 and 9-11)
- Read and Study:
- 9-4 and 9-5
- Work:
- Ch 9 #68-71, 73
- Answers: 68) (a) v = 3.95 m/s, (b) 49.3 rad/s 70) v = 2.79 m/s,
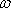 = 34.9 rad/s
= 34.9 rad/s
Wed, Mar 31
(Mr. S absent)
Work Day
- Catch up on your assignments.
9-6 Rolling Objects
- "Rolling without slipping" concepts
- the role of friction
- motion of:
- the point of contact between the wheel and surface
- the center of the wheel
- the top of the wheel
- rotation about:
- point of contact
- center of the wheel (rotation + translation)
- Kinetic energy of a rolling object
- Objects rolling up and down inclines
- Who wins the race between a disk, a sphere, and a hoop?
- Conservation of Energy approach
- Newton's Second Law approach (What is the friction force?)
- Rolling with slipping - the bowling ball problem
- initial conditions - the effect of friction
- time for which
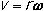
- Read:
- 9.6
- Work:
- Ch 9 #79-87odd
Chapter 10 Conservation of Angular Momentum
- 10-1 The Vector Nature of Rotation (review for us)
- Right-hand rule
- Cross product
- 10-2 Torque and Angular Momentum
- Angular Momentum, L, of a particle
- For a particle moving in a circle, p = mv, so we would like
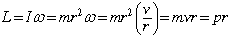 .
. - In general,
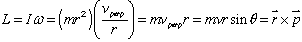
- direction of L - use right-hand rule
-
Linear Rotational 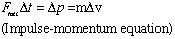
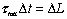
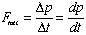 (see note 1)
(see note 1) 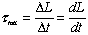 (see note 2)
(see note 2) 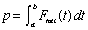
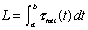
- Note 1: This is Newton's Second Law:
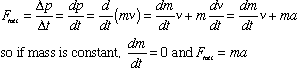
- Note 2: This is Newton's Second Law for Rotation:
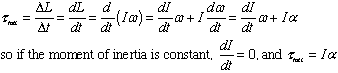
- For a particle moving in a circle, p = mv, so we would like
- Angular Momentum, L, of a particle
- Read:
- 10-1 and 10-2
- Answer:
- Ch. 10 #1-9odd, 43-46
- Answers: 44a) 28.0 kg m2/s, 44b) 32 kg m2, 44c) 0.875 rad/s
Ch 10 Conservation of Angular Momentum
- 10-3 Conservation of Angular Momentum
- From Newton's 2nd Law for Rotation:
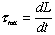 , so if the net torque on an object (system) is zero, the rate of change of its angular momentum will be zero.
, so if the net torque on an object (system) is zero, the rate of change of its angular momentum will be zero. - In other words, if the net torque on a system is zero, its angular momentum will not change.
- Skaters and divers
- From Newton's 2nd Law for Rotation:
- Conservation of Angular Momentum in a bicycle wheel
- Vector nature of angular momentum
- Summary of Linear and Rotational Dynamics Equations
- Read:
- 10-3
- Work:
- Ch 10 #12, 49, 51, 55, 57
Ch 11 Gravity
- 11-1 Kepler’s Laws
- First Law - Orbits are ellipses with sun at one focuw
- Second Law - Radius vector sweeps out equal areas in equal times
- Third Law - T2 = kr3
- mean distance = length of semi-major axis
- 11-2 Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
- Derivation of Kepler's Laws
- 11-3 Gravitational Potential Energy
- Using a graph of gravitational potential energy
- Escape energy
- Escape velocity
- Energy in a circular orbit
- 11-4 The Gravitational Field and g
- g as a measure of gravitational field strength
- Read:
- Ch 11
- Work:
- Ch 11 #1-9odd, 15, 17, 21, 23, 37, 43-49odd, 53, 57, 59
Wed, Apr 7
- Finish the Ch 11 assignment
Thu, Apr 8
Fri, Apr 9
Mon, Apr 12
Tue, Apr 13
Ch 12 - Static Equilibrium
- Conditions for static equilibrium:
- Fnet = 0 in both the x and y directions
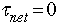 about any axis
about any axis
- Examples
- Read:
- 12-1 - 12-3
- Work:
- Ch 12 #1, 2 (ans: false), 9, 14 (ans: 1.4 m), 28 (ans: (a) Forces are T1, T2, and FH, (b) 139 N), 49
Wed, Apr 14
Ch 14 Oscillations
- Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
- If the net force on an object is a Hooke's Law force (Fnet = -kx), the object will move in simple harmonic motion.
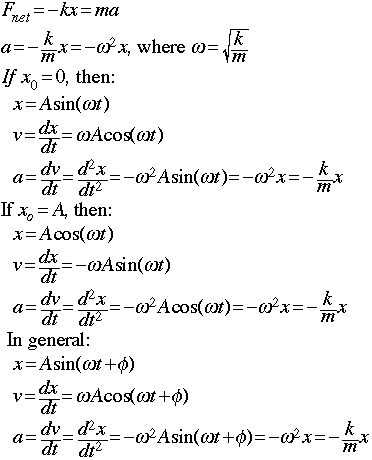
- Where:
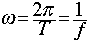
- SHM and circular motion
- Examples
- Read:
- 14-1
- Work:
- Ch. 14 #1, 3, 23-27 odd
Thu, Apr 15
Ch 14 Oscillations
- 14-2 Energy in SHM
- 14-3 Some Oscillating Systems
- The simple pendulum
- The physical pendulum
- Read:
- 14-2 and 14-3
- Work (The last assignment in AP Physics):
- Ch 14 #57, 60. 61, 67
Fri, Apr 16
Convo Schedule:
3rd block: 12:14-1:19
P.P.: 1:19-1:25
4th block: 1:25-2:30
Ketchup Day
Finish up your assignments.
Mon, Apr 19
Tue, Apr 20
Wed, Apr 21
Thu, Apr 22
Fri, Apr 23
Mon, Apr 26
Tue, Apr 27
Wed, Apr 28
End of A4 - 20 days