BHS -> Mr. Stanbrough -> Physics -> Mechanics -> Newton's Laws -> Newton's First Law -> this page
To use an inertial balance to measure the masses of objects.
"Mass: The quantity of matter in a body. More specifically, it is a measure of the inertia or "laziness" that a body exhibits in response to any effort made to start it, stop it, or change in any way its state of motion."2
 Scientists
measure things. A scientific question to ask is, "This definition of
mass is very nice, but how can mass be measured?" There are several
ways to measure mass - a triple-beam balance measures mass, for
instance. The triple-beam balance has a couple of disadvantages,
however. First, it is difficult to see how the measurement you make
on a balance correlates to the definition of mass given above, and
the triple-beam balance won't work where there is no gravity.
Scientists
measure things. A scientific question to ask is, "This definition of
mass is very nice, but how can mass be measured?" There are several
ways to measure mass - a triple-beam balance measures mass, for
instance. The triple-beam balance has a couple of disadvantages,
however. First, it is difficult to see how the measurement you make
on a balance correlates to the definition of mass given above, and
the triple-beam balance won't work where there is no gravity.
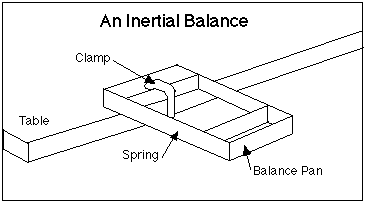
If mass measures the "laziness" of an object in response to efforts made to change its velocity, it makes sense that you should be able to measure mass by making an effort to change the velocity of an object and recording its "laziness." This is what an inertial balance does. It uses two strips of spring steel to apply the same "effort" in order to vibrate it back and forth. (A vibration involves speeding up, slowing down, and changing direction, so the state of motion of the object is certainly changed.) If the object vibrates quickly it is not "lazy" - it does not have much mass. Objects that vibrate slowly have a large mass.
By measuring how fast known masses vibrate on the inertial balance, you can construct a graph that "calibrates" the balance - that is, if you know how quickly an unknown mass vibrates you can use the graph to determine its mass.
|
inertial balance |
stopwatch |
|
C-clamp |
graph paper |
|
set of standard masses |
masking tape |
|
"unknown" masses |
NOTE: You will work with one or more lab partners in this lab. You are responsible to turn in INDIVIDUAL lab reports, however. Your lab report should include a data table, your graph, results for the "unknowns," and analysis.
The instructor will demonstrate how to set up the inertial balance. Be sure to clamp one end of the balance to the table so that the other end is free to vibrate freely in the air beside the table. When you place objects in the balance pan, you will need to use masking tape to keep them from sliding about in the pan.
The point of calibrating the inertial balance is to come up with a graph that shows the response of the balance when a range of masses is placed in it. To do this, you will need to do some careful planning. Here are some hints and pointers:
The point of the lab is to demonstrate that you can measure the mass of an object using the inertial balance. Your instructor will place several objects of "unknown mass" where you have access to them. Determine the mass of at least 2 of them using your inertial balance. Some hints:
Draw a graph of (known) mass versus the response measure you have chosen. Draw the best smooth curve through your data points. Use your graph to determine the masses of your unknowns.
2Hewitt, Paul, Conceptual Physics, Second Edition, 1992, p. 32