Curved Mirror Questions,
Exercises, & Problems
![[Up]](../../NavIcons/Up.GIF)
![[Home]](../../NavIcons/Home.GIF)
![[Help]](../../NavIcons/Help.GIF)
- A converging (concave) mirror is cut from a sphere whose
radius is 20 cm. What will be the focal length of the mirror?
- Explain the difference between a real image and a virtual
image.
- What type of image is produced by a plane mirror? Can it ever
produce the other type? Defend your answer.
- Explain when a concave mirror produces a real image and when
it produces a virtual image.
- Will a convex mirror ever produce a real image? Defend your
answer.
- A concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 24 cm. An object
3 cm. tall is placed in front of the mirror. Use a ray diagram to
locate the image of the object and then describe the image (type,
size, right-side up or upside down) if the object is located:
- 48 cm from the mirror
- 30 cm. from the mirror
- 24 cm. from the mirror
- 16 cm. from the mirror
- 6 cm. from the mirror
- Use equations 1 and 2 to locate and describe the images for
the previous problem.
- A convex mirror has a radius of curvature of 24 cm. If an
object 6 cm. tall is placed 6 cm. from the front of the mirror,
describe the image using:
- a ray diagram.
- Equations 1 and 2
- The mirror of the Mount Palomar telescope has a diameter of
5.0 m. How many times more light does this telescope gather than a
telescope half as big (with a diameter of 2.5 m.)?
- When you look through an astronomical reflecting telescope,
will the image you see be right-side up or inverted? Why?
- Can the image produced by a concave mirror ever appear between
the focus of the mirror and the mirror? Defend your answer.
- The positions of objects and images are often expressed in
terms of their distance from the vertex of a concave mirror,
rather than in terms of their distance from the focus. Suppose
that we call So is the distance between the object and
the mirror and Si the distance between the image and
the mirror. Then, Do = So - f, and
Di = Si - f. Show that Equation 2
(Di= f2/Do) can then be written
as:
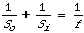
- A concave mirror produces an image if the object is just
outside the focus, and an image if the object is just inside the
focus. Where are these images? Why is no image produces at the
focus?
![[Up]](../../NavIcons/Up.GIF)
![[Home]](../../NavIcons/Home.GIF)
![[Help]](../../NavIcons/Help.GIF)
last update October 21, 1999 by JL
Stanbrough